Creatine: The Most Underrated Anti-Aging Supplement
New research shows it fuels your neurons as much as your biceps — and maybe your memory, too
Creatine used to be the stuff of gym bros and locker-room legends — cheap white powder to make muscles pop. But science has caught up, and it’s rewriting the story. Turns out, creatine isn’t just about muscle mass. It’s also brain fuel.
Subconscious Fat at 30,000 Feet
Recent research indicates that creatine supplementation enhances cognition, working memory, and mental resilience — particularly as we age. And the latest twist? The brain may need more creatine than we thought — closer to 8–10 grams daily — to reach its full potential.
Mr. Skeptical lifted one eyebrow, the international symbol for ‘Yeah Right’. “Ten grams? What’s next, a creatine IV drip?”
“Not yet. But the evidence suggests your neurons might appreciate the extra scoop.”
Subconscious Fat at 10,000 Feet
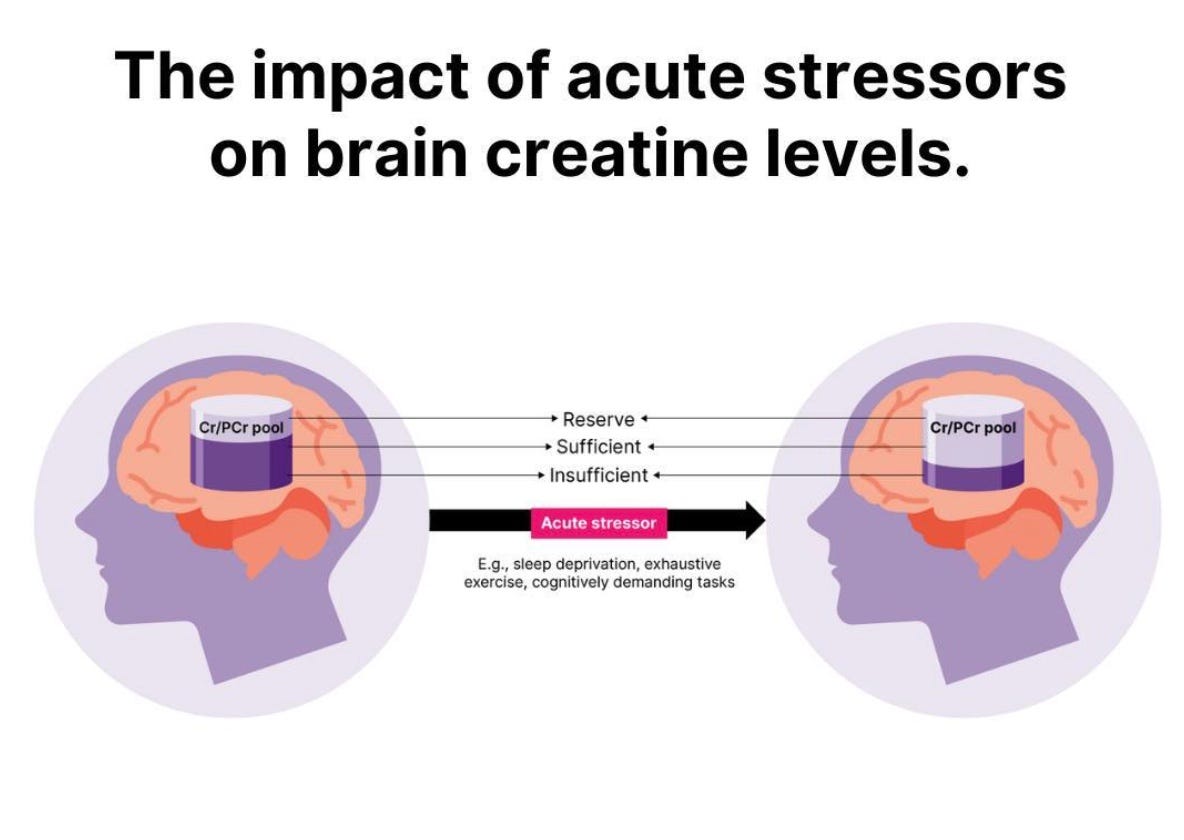
Creatine’s main gig is ATP recycling — giving your cells quick energy to burn. Most people know that happens in muscle, but neurons are just as energy-hungry. Your brain burns roughly 20 percent of your body’s total energy, even when you’re doing nothing. Under sleep loss, stress, or aging, that demand spikes — and ATP production can’t always keep up.
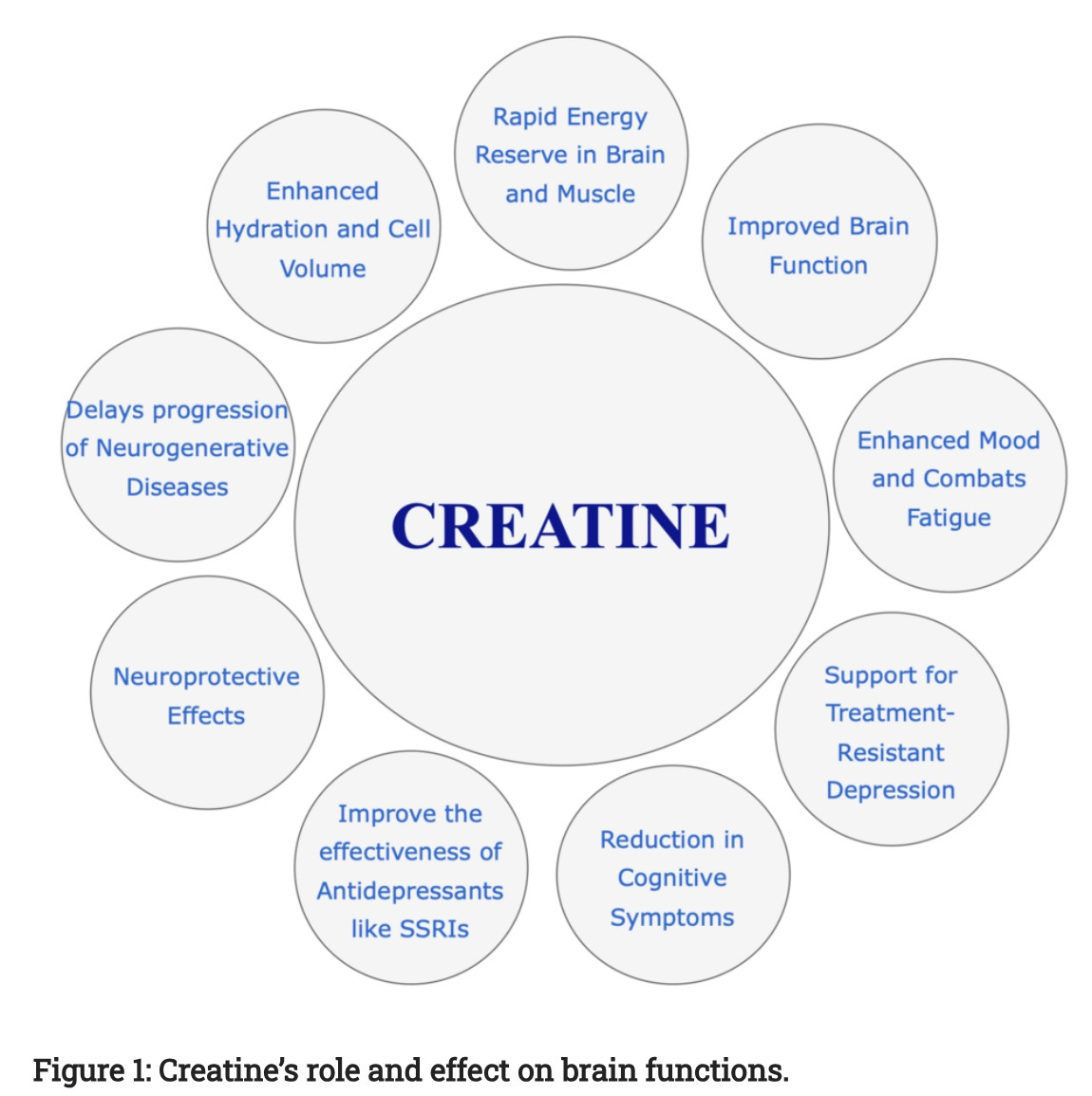
Enter creatine. It acts as an energy buffer, maintaining ATP levels when neurons start running low. A 2023 review in Nutrients found that supplemental creatine improved reasoning, memory, and reaction time under conditions of mental fatigue. Another 2022 Frontiers in Nutrition meta-analysis concluded the same thing: creatine enhances cognitive performance, especially when the brain’s stressed.
Now here’s where it gets interesting: several newer studies — including a 2023 Amino Acids paper — found that 5 grams may not be enough to saturate brain tissue, even after weeks of use. Higher daily intakes, around 8–10 grams, consistently raised brain creatine levels and correlated with stronger cognitive effects.
Mr. Skeptical leans back, lips pushed out like he’s trying to kiss a ghost. “So, my brain’s a creatine hog now? Great. Another organ demanding attention.”
“Pretty much. It’s like your neurons are training for a marathon you didn’t sign up for.”
Subconscious Fat at Eye-Level
Aging makes this whole process even more critical. Natural creatine stores in both muscle and brain decline with age, and older adults often (unwisely) eat less meat, the primary dietary source of creatine. Let me repeat that, creatine is found in meat and animal products.
Mr. Skeptical puts up his hands in protest. “I know creatine is found in animal products.”
I can’t help but add, “And it’s not found at all in any vegetables or plants, not even in trace amounts.”
Mr. Skeptical folds his arms and pouts, like a baby who’d gotten his toy taken away.
Feeling good, I continue…
A 2021 Aging Cell MRI study found that creatine concentrations decrease in key brain regions associated with memory and planning. When older adults were supplemented, results improved. One Psychopharmacology (2022) trial using 10 grams per day for six weeks showed measurable boosts in reasoning, short-term memory, and reaction time.
It’s not magic — it’s metabolic maintenance. The extra creatine restores what time, diet, and stress quietly erode.
Mr. Skeptical holds up his hands showing his 10 fingers, “Ten grams daily, huh? Sounds like I’ll need a bigger spoon.”
“Think of it less like dosing a supplement and more like topping off your brain’s battery.”
Practical Suggestions and Conclusions
If you’re already using creatine, great — you’re doing more for your cognition than most people realize. But if you’ve been sticking to the old “5 grams forever” playbook, the latest data suggest you might get better brain benefits by going a little higher.
What the research suggests now:
For muscle: 3–5 grams daily still works perfectly.
For brain and cognitive health: 8–10 grams daily may be needed to achieve brain saturation (split into two doses if you prefer).
Form: Stick with plain creatine monohydrate. Fancy versions haven’t proven better.
Timing: Whenever you remember to take it — consistency is king.
Safety data remain excellent. Even at 10 grams per day, long-term studies show no adverse effects in healthy adults with normal kidney function.
Mr. Skeptical adds, “So the new rule is: twice the powder, twice the power?”
“Exactly. However, I wouldn’t put that on the label unless you want to risk a lawsuit. Creatine is one of those rare compounds that continues to improve the more we study it. What started as a muscle supplement has become a cognitive ally — cheap, safe, and quietly powerful.”
“So… creatine for my body and my brain. Does it fix my personality, too?”
“Sorry, no supplements that strong.”
Be aware.
Other links related to this post:
Is Creatine Worth Taking?
Does What We Eat Affect Mental Health?
Context
PS Links on LinkedIn, Facebook, Instagram, X, and Notes. Full disclosure: ChatGPT was used to research and enhance this post.



Great info. Where do you order your Creatine from?